Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's View On Investor Concerns
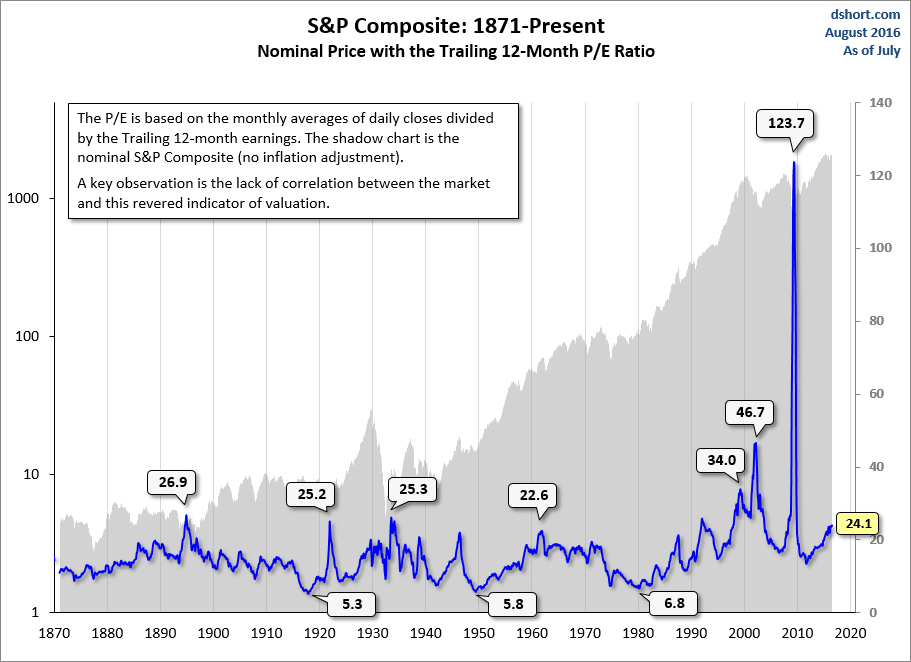
Table of Contents
BofA's Current Market Outlook and Valuation Concerns
BofA's assessment of the current market conditions often reflects a nuanced perspective, neither purely bullish nor bearish, but rather a cautious optimism adjusted to prevailing economic indicators. Their outlook is heavily influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Currently, they might be leaning slightly toward cautious optimism, depending on the specific report and timing. This is primarily driven by factors like inflation rates, interest rate hikes from central banks like the Federal Reserve, and global geopolitical instability.
- Bullet Points:
- Summary of BofA's recent reports on market valuations: BofA's recent reports often highlight a need for careful consideration of valuations, suggesting that while opportunities exist, a selective and strategic approach is necessary. They frequently analyze the potential for corrections in overvalued sectors.
- Key economic indicators influencing BofA's view: Inflation, interest rate adjustments, and GDP growth are consistently highlighted by BofA as key factors determining market valuations and overall investor sentiment. Unexpected changes in any of these areas can significantly influence their outlook.
- Specific sectors BofA highlights as overvalued or undervalued: BofA's reports often pinpoint specific sectors, such as technology or energy, as potentially overvalued or undervalued based on their valuation models and predicted future growth. These assessments can change based on economic shifts.
- Mention any specific companies BofA has commented on: BofA analysts frequently comment on specific companies, offering insights into their individual valuations and potential for future growth. These insights usually form part of broader market analysis and sector-specific reports.
Key Valuation Metrics and Their Interpretation
Several key valuation metrics are crucial for assessing the stock market's health and individual company prospects. Understanding these metrics allows investors to make more informed decisions.
- Bullet Points:
- Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E): Calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS), this ratio indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company's earnings. A high P/E ratio might suggest overvaluation, while a low P/E might indicate undervaluation, but context is crucial.
- Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S): Calculated by dividing the market capitalization by the company's revenue, the P/S ratio is useful for valuing companies with negative earnings or those in early growth stages.
- Price-to-Book ratio (P/B): This metric compares a company's market value to its book value (assets minus liabilities). A high P/B ratio may suggest the market perceives the company as having strong future growth potential.
- Dividend Yield: Calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock price, this metric indicates the percentage return an investor receives from dividends. It's useful for income-focused investors.
- How each metric relates to investor sentiment and market health: High P/E ratios generally reflect optimistic investor sentiment and expectations of future growth. Conversely, low P/E ratios might suggest pessimism or undervalued stocks.
Understanding the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E)
The P/E ratio is arguably the most widely used valuation metric. It represents the price investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings.
- Bullet Points:
- Factors that affect P/E ratios: Growth prospects, risk profile, interest rates, and industry trends all significantly impact a company's P/E ratio. High-growth companies typically command higher P/E ratios.
- How to use P/E ratios to compare companies within the same industry: Comparing P/E ratios within the same industry provides a more meaningful comparison than comparing across vastly different sectors. A company with a significantly higher P/E than its peers within the same industry might be overvalued.
- Limitations of solely relying on P/E ratios for valuation: The P/E ratio should not be the sole determinant of a stock's valuation. Other factors, such as debt levels, future growth prospects, and industry trends, must be considered.
Addressing Investor Concerns Based on BofA's Analysis
Investor concerns often center on macroeconomic factors and geopolitical events. BofA's analysis helps contextualize these anxieties within the broader framework of stock market valuations.
- Bullet Points:
- How BofA incorporates these concerns into their valuation models: BofA uses sophisticated models that incorporate various economic indicators, including inflation forecasts, interest rate expectations, and GDP projections, into their valuation analyses.
- Specific strategies BofA suggests for mitigating these risks: BofA might suggest strategies like diversification, hedging, and investing in less volatile asset classes to mitigate the risks associated with inflation, recession fears, or geopolitical uncertainty.
- Addressing the impact of these concerns on different asset classes: The impact of inflation, for instance, might vary across asset classes. BofA's analysis often highlights these differences, helping investors make informed choices based on risk tolerance and investment goals.
Practical Strategies for Investors Based on BofA's Insights
BofA's analysis provides actionable advice for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of stock market valuations.
- Bullet Points:
- Diversification strategies to manage risk: Diversifying across different sectors, asset classes, and geographies is crucial to reduce portfolio risk. BofA often stresses the importance of diversification in their recommendations.
- Sector-specific investment recommendations: Based on their valuation models and market outlook, BofA may suggest specific sectors that appear undervalued or offer attractive growth potential.
- Long-term vs. short-term investment approaches: BofA might advocate for a long-term investment strategy, emphasizing that market fluctuations are normal and focusing on long-term growth potential. Short-term trading requires different strategies and risk management.
- Importance of regular portfolio review and adjustments: Regularly reviewing and adjusting your investment portfolio based on changing market conditions and new information is vital.
Conclusion
Understanding stock market valuations is a critical skill for any investor. BofA's analysis provides valuable insights into current market conditions and investor concerns. By understanding key valuation metrics like the P/E ratio and considering BofA's perspective on prevailing economic factors, investors can make more informed decisions. Remember to regularly review your investment strategy and adapt it based on evolving market conditions and expert opinions, like those provided by BofA. Stay informed about stock market valuations and continue to refine your investment approach to achieve your financial goals. Learn more about effective stock valuation strategies and build a robust investment portfolio.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Canadas Fiscal Health Sustainable Examining Liberal Spending
Apr 24, 2025
Is Canadas Fiscal Health Sustainable Examining Liberal Spending
Apr 24, 2025 -
 India Market Buzz Niftys Bullish Run Fueled By Positive Trends
Apr 24, 2025
India Market Buzz Niftys Bullish Run Fueled By Positive Trends
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Navigate The Private Credit Boom 5 Dos And Don Ts To Land Your Dream Job
Apr 24, 2025
Navigate The Private Credit Boom 5 Dos And Don Ts To Land Your Dream Job
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Zagonetka Tarantina Razotkrivena Prica Iza Odbijenog Filma S Travoltom
Apr 24, 2025
Zagonetka Tarantina Razotkrivena Prica Iza Odbijenog Filma S Travoltom
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Ai Digest Creating A Poop Podcast From Repetitive Documents
Apr 24, 2025
Ai Digest Creating A Poop Podcast From Repetitive Documents
Apr 24, 2025
