U.S.-China Relations: A Breakdown And The Looming Threat Of A New Cold War

Table of Contents
Economic Competition and the Trade War
The economic relationship between the U.S. and China has been a defining feature of globalization, but it has also become a major source of tension. The trade war, initiated during the Trump administration, represents a significant shift away from previous patterns of cooperation. Keywords: Trade war, tariffs, economic sanctions, trade deficit, intellectual property theft, supply chains.
- The origins of the trade war: The trade war stemmed from longstanding U.S. concerns about China's trade practices, including allegations of intellectual property theft, forced technology transfer, and a persistent trade deficit. The Trump administration imposed tariffs on hundreds of billions of dollars worth of Chinese goods, triggering retaliatory measures from Beijing.
- Impact of tariffs: Tariffs imposed by both sides significantly impacted global supply chains, increasing costs for businesses and consumers in both countries. The economic consequences were felt across various sectors, disrupting established trade relationships and prompting companies to re-evaluate their global supply chain strategies.
- Intellectual property disputes: Disputes over intellectual property rights and technology transfer remain a core point of contention. The U.S. accuses China of systematically stealing intellectual property and forcing foreign companies to share their technology in exchange for access to the Chinese market. These accusations have fuelled concerns about unfair competition and the erosion of American technological advantage.
- Decoupling and supply chain restructuring: The trade war accelerated efforts to decouple the U.S. and Chinese economies, leading to a restructuring of global supply chains. Companies are diversifying their sourcing and manufacturing operations to reduce reliance on either country, a process that has both economic and geopolitical implications.
- Potential for future escalation: The potential for future escalation of economic sanctions remains significant. Further restrictions on technology exports, investment limitations, and other economic measures could deepen the divide and further exacerbate geopolitical tensions. This economic warfare could significantly harm global economic growth.
The trade war represents more than just a tariff dispute; it's a symptom of deeper structural issues within the U.S.-China relationship, highlighting the challenges of managing economic interdependence amid strategic competition.
Technological Rivalry and the Race for Supremacy
Beyond economic competition, a fierce technological rivalry is shaping the future of U.S.-China relations. This competition is playing out across various sectors, raising concerns about national security, economic dominance, and global technological leadership. Keywords: Technological rivalry, 5G, artificial intelligence, semiconductors, technological decoupling, cybersecurity.
- Competition in key sectors: The competition is most intense in strategically important areas such as 5G telecommunications, artificial intelligence (AI), and semiconductors. Both countries are investing heavily in research and development, seeking to establish technological dominance in these fields.
- Technological espionage: Concerns about Chinese technological espionage and intellectual property theft have intensified, adding another layer of complexity to the already strained relationship. These concerns have fueled calls for greater protection of intellectual property and stricter regulation of technology transfer.
- Technological decoupling implications: The push for technological decoupling, particularly in sensitive areas such as semiconductors, carries significant implications for innovation and economic growth globally. It could lead to the fragmentation of the global technology ecosystem and hinder collaborative research and development.
- Government support and investment: Both governments play a significant role in shaping technological competition through substantial investments in research, development, and subsidies for domestic industries. This state-sponsored competition exacerbates the already tense rivalry.
- Cybersecurity risks: Increased technological interdependence also carries significant cybersecurity risks. The potential for cyberattacks and data breaches increases as the technological relationship between the two countries becomes more intertwined.
The race for technological supremacy is a defining characteristic of the current U.S.-China relationship and will likely continue to shape the geopolitical landscape for years to come.
Geopolitical Tensions and Regional Conflicts
Beyond economic and technological factors, geopolitical tensions and regional conflicts further strain U.S.-China relations, creating a volatile environment prone to miscalculation. Keywords: Taiwan, South China Sea, human rights, Indo-Pacific strategy, military buildup, regional alliances.
- Taiwan's status: The issue of Taiwan's status remains a major source of tension. China considers Taiwan a breakaway province and has not ruled out the use of force to achieve reunification. The U.S. maintains a policy of "strategic ambiguity" regarding its commitment to defend Taiwan, adding to the uncertainty.
- South China Sea disputes: China's assertive actions in the South China Sea, including its construction of artificial islands and its claims to vast swathes of the maritime territory, have heightened tensions with neighboring countries and the U.S. These disputes have significant implications for regional stability and freedom of navigation.
- Human rights concerns: The human rights situation in Xinjiang and Hong Kong has become a significant point of contention. U.S. criticism of China's human rights record has strained relations and led to reciprocal accusations.
- Indo-Pacific strategy: The U.S. Indo-Pacific strategy, aimed at countering China's growing influence in the region, has further aggravated tensions. This strategy involves strengthening alliances, boosting military presence, and promoting economic cooperation among partner countries.
- Military buildup and escalation: The military buildup by both countries contributes to a heightened sense of insecurity and increases the risk of miscalculation and accidental conflict. The potential for military escalation and proxy conflicts is a serious cause for concern.
These geopolitical flashpoints underscore the fragility of peace in the region and the importance of diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions and prevent conflict.
The Risk of Miscalculation and Escalation
The complex interplay of economic, technological, and geopolitical factors increases the risk of miscalculation and unintended escalation. Keywords: Military escalation, accidental war, miscalculation, arms race, deterrence.
- Dangers of miscalculation: The potential for miscalculation and accidental conflict is a significant concern. Misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and unintended actions could easily escalate into a major crisis.
- Arms race and heightened tensions: The ongoing military buildup by both countries contributes to an arms race and fuels a climate of heightened tensions, increasing the risk of conflict.
- Communication and risk reduction: Effective communication and risk-reduction mechanisms are essential to preventing accidental conflict. Establishing clear communication channels and building trust are crucial to reducing the risk of miscalculation.
- Proxy conflicts: The potential for proxy conflicts to escalate into a direct confrontation between the U.S. and China is a real possibility. Regional conflicts and disputes could easily draw both superpowers into a wider conflict.
The need for careful diplomacy, effective communication, and robust risk-reduction mechanisms cannot be overstated.
Conclusion
The relationship between the United States and China is at a critical juncture. Economic competition, technological rivalry, and geopolitical tensions are all contributing to a heightened risk of a new Cold War. Understanding the complexities of this relationship is crucial to mitigating potential conflict. The future of U.S.-China relations requires careful navigation and a commitment to diplomacy. We must find ways to manage competition while avoiding the pitfalls of a new Cold War. Further research and informed discussion on U.S.-China relations are essential to fostering a more peaceful and prosperous future for all. Failing to address the underlying tensions and find pathways to cooperation could lead to disastrous consequences. Let's work towards a future where Sino-American relations are characterized by cooperation rather than confrontation.

Featured Posts
-
 Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Production To A Halt
Apr 22, 2025
Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Production To A Halt
Apr 22, 2025 -
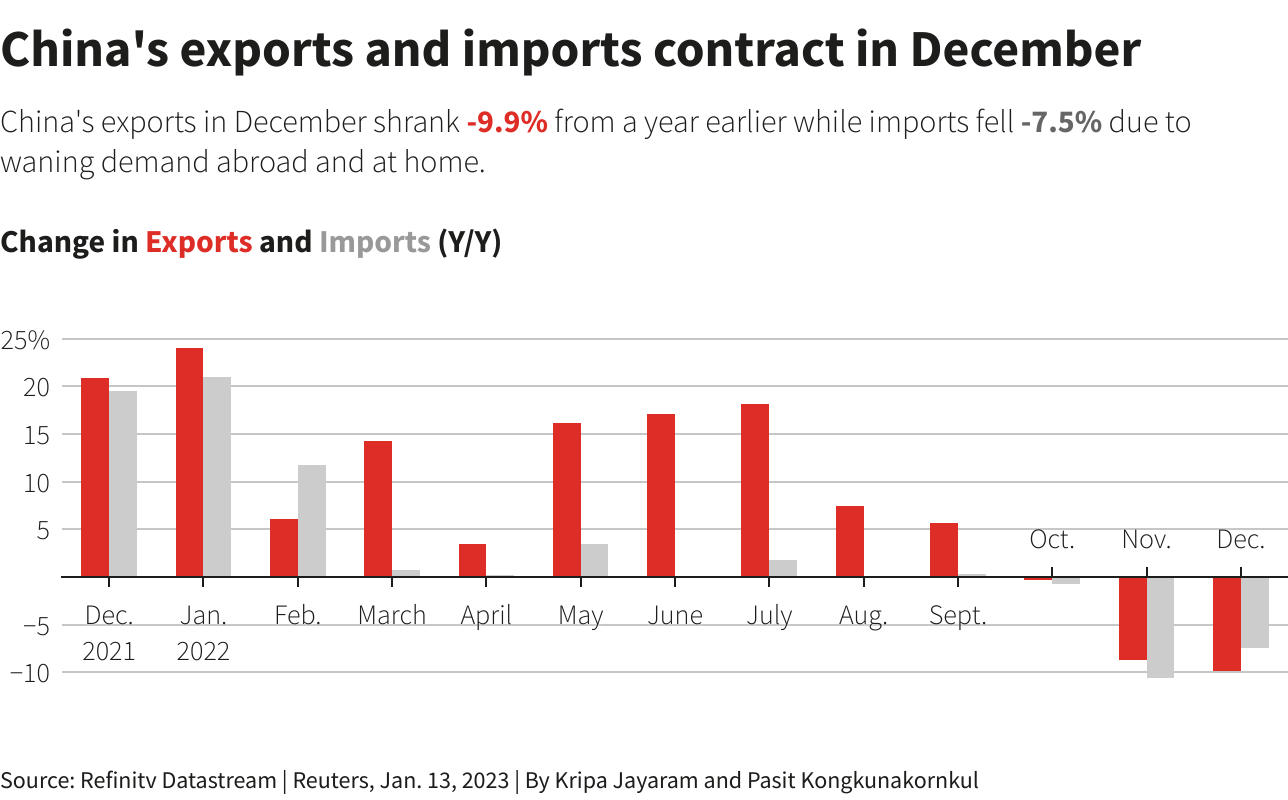 Chinas Export Dependence Vulnerability To Tariff Hikes
Apr 22, 2025
Chinas Export Dependence Vulnerability To Tariff Hikes
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Conclave 2023 Assessing Pope Francis Enduring Impact
Apr 22, 2025
Conclave 2023 Assessing Pope Francis Enduring Impact
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Section 230 And Banned Chemicals On E Bay A Judges Ruling
Apr 22, 2025
Section 230 And Banned Chemicals On E Bay A Judges Ruling
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Months Long Impact On Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Months Long Impact On Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
