China's Export Dependence: Vulnerability To Tariff Hikes
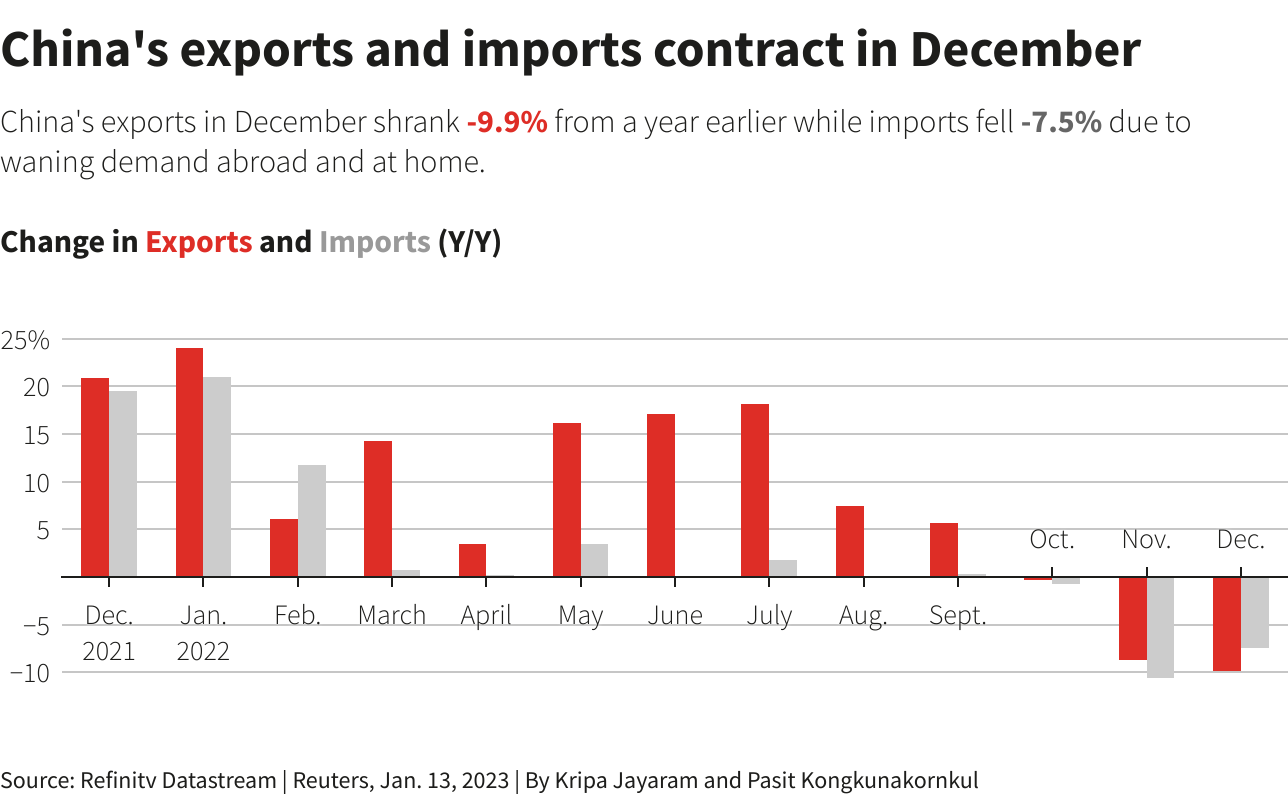
Table of Contents
The Magnitude of China's Export Dependence
China's economy is undeniably export-oriented. For years, exports have constituted a substantial portion of its GDP, contributing significantly to its economic growth and creating millions of jobs. Understanding the sheer scale of this dependence is crucial to grasping the potential ramifications of trade disruptions.
-
Percentage of GDP from exports over the last decade: While the exact percentage fluctuates yearly, exports have consistently contributed over 20% to China's GDP for the past decade, a figure significantly higher than many other major economies. This reliance highlights the critical role exports play in China's economic health.
-
Key export sectors and their contribution to overall exports: Manufacturing, particularly electronics and machinery, forms the backbone of China's export engine. Technology exports, including telecommunications equipment and computer components, have also grown rapidly in recent years. These sectors' dominance underscores the vulnerability inherent in concentrating export efforts within a relatively limited range of industries.
-
Comparison with other major exporting nations: Compared to other major global exporters like Germany or the United States, China's export dependence remains exceptionally high, illustrating a greater sensitivity to external trade shocks and tariff fluctuations. This stark difference highlights the need for China to actively diversify its economic foundation.
The Impact of Tariff Hikes on Chinese Exports
The imposition of tariffs, particularly retaliatory tariffs in trade wars, significantly impacts Chinese exports. Tariffs increase the cost of Chinese goods in foreign markets, leading to reduced demand and potentially harming China's export market share.
-
Examples of past tariff impacts on specific Chinese industries: The US-China trade war provided a stark illustration of this. Tariffs on Chinese goods led to decreased sales in certain sectors, impacting manufacturers and disrupting supply chains. This ripple effect cascaded throughout the Chinese economy.
-
Discussion of potential supply chain disruptions due to tariffs: Tariffs don't just affect final goods; they disrupt entire supply chains. If Chinese component manufacturers face higher tariffs, the cost of producing goods worldwide, including those made in other countries, rises, leading to further economic instability.
-
Analysis of the impact on Chinese export market share in various regions: Tariff hikes have visibly affected China's export market share in key regions like the US and Europe, necessitating a strategic reevaluation of trade relationships and diversification into new markets.
-
Exploration of China's retaliatory trade measures and their effectiveness: China has employed its own retaliatory measures, but their overall effectiveness in mitigating the negative impact of tariffs remains a subject of ongoing debate among economists.
Vulnerability of Specific Export Sectors
Certain export sectors are inherently more vulnerable to tariff hikes than others. A targeted approach to assessing these vulnerabilities is critical for developing effective mitigation strategies.
-
Analysis of the vulnerability of the technology sector to US tariffs: The technology sector, a crucial component of China's export strategy, is particularly sensitive to tariffs imposed by major technology consumers. These tariffs can severely limit market access and hinder technological advancement.
-
Impact of tariffs on Chinese manufacturing exports to Europe and other regions: While the US is a key trading partner, the impact of tariffs extends to other regions. Increased costs associated with tariffs can hinder competitiveness in European and other international markets.
-
The effect of tariffs on agricultural exports and food security: Though less prominent than manufacturing, agricultural exports are also vulnerable to trade restrictions. Tariffs impacting agricultural products could not only affect export revenue but also potentially impact domestic food security.
Strategies for Mitigating Export Dependence
To enhance its economic resilience, China needs to proactively reduce its reliance on exports and foster a more balanced economic structure. This requires a multi-faceted approach.
-
Strategies to stimulate domestic consumption and reduce reliance on foreign markets: Government policies aimed at raising disposable incomes and fostering a robust domestic consumer market are crucial in reducing reliance on exports.
-
Initiatives to encourage foreign direct investment (FDI) in non-export sectors: Attracting FDI into sectors less dependent on exports can help diversify the economy and create a more stable economic foundation.
-
Government policies to promote technological innovation and industrial upgrading: Investing in R&D and supporting the development of high-value-added industries will allow China to compete more effectively in global markets, less reliant on price-based competition and more on innovation and technology.
-
The role of economic diversification in reducing vulnerability to external shocks: Diversifying into new sectors and markets creates buffers against external shocks, including tariff hikes and fluctuating global demand. This reduces the risk of significant economic downturn in response to external trade disputes.
Conclusion
China's significant export dependence creates a substantial vulnerability to tariff hikes and other trade disruptions. The impact on specific sectors, from technology to manufacturing and agriculture, is considerable, posing a threat to both economic growth and job security. To mitigate this risk, China must prioritize strategies to stimulate domestic consumption, attract foreign direct investment in diverse sectors, promote technological innovation, and ultimately reduce its overall export dependence. Understanding China's export dependence and analyzing the impact of tariff hikes on China is crucial for informed decision-making on trade policy. Explore strategies to reduce export dependence and build a more resilient, diversified Chinese economy.

Featured Posts
-
 New Signal Chat Exposes Hegseths Pentagon Chaos Claims
Apr 22, 2025
New Signal Chat Exposes Hegseths Pentagon Chaos Claims
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Luxury Automakers Face Headwinds In China Case Studies Of Bmw And Porsche
Apr 22, 2025
Luxury Automakers Face Headwinds In China Case Studies Of Bmw And Porsche
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Hollywood Shut Down Actors And Writers On Strike What It Means For Film And Tv
Apr 22, 2025
Hollywood Shut Down Actors And Writers On Strike What It Means For Film And Tv
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Dow Futures Drop Live Stock Market Updates And Analysis
Apr 22, 2025
Dow Futures Drop Live Stock Market Updates And Analysis
Apr 22, 2025 -
 16 Million Penalty For T Mobile Three Years Of Unreported Data Breaches
Apr 22, 2025
16 Million Penalty For T Mobile Three Years Of Unreported Data Breaches
Apr 22, 2025
