Tesla's Optimus Project Faces Headwinds: Rare Earth Supply Chain Disruptions From China
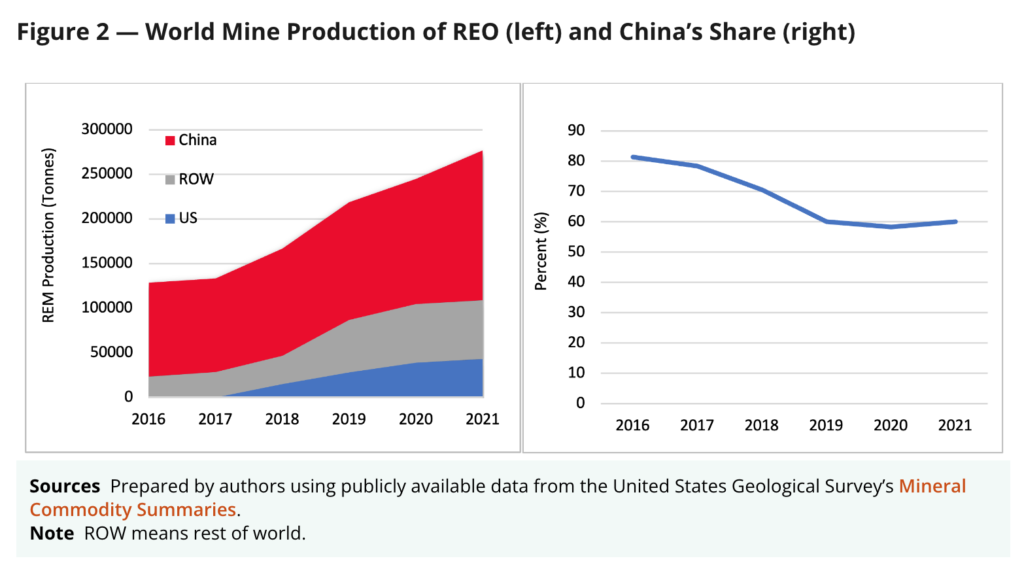
Table of Contents
China's Monopoly on Rare Earth Minerals
The success of advanced robotics, including Tesla's Optimus, hinges on the availability of rare earth elements (REEs). These elements, including neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, are crucial for creating powerful and efficient motors, sensors, and other essential components.
The Critical Role of Rare Earths in Robotics
REEs possess unique magnetic and electronic properties unmatched by readily available alternatives. Their use in Optimus is vital for:
- High-performance motors: REEs are essential for creating the small, powerful, and efficient motors that drive Optimus's limbs and enable its precise movements. Neodymium magnets, for instance, are critical for achieving the necessary torque and speed.
- Advanced sensors: Many of Optimus's sensors rely on REEs for their functionality. These sensors are essential for navigation, object recognition, and interaction with its environment.
- Actuators and control systems: The precise control of Optimus's movements requires actuators and control systems that benefit significantly from the unique properties of REEs.
These applications highlight the superior performance characteristics offered by REEs compared to alternative materials. Replacing them would necessitate significant technological breakthroughs and likely compromise Optimus's capabilities and efficiency.
China's Dominance in Mining and Processing
China currently controls a vast majority of the global rare earth mining and processing capacity. This dominance stems from:
- Significant reserves: China possesses substantial deposits of rare earth minerals, giving it a considerable head start in mining operations.
- Technological advantage: China has invested heavily in developing advanced technologies for extracting and processing REEs, leading to a significant cost advantage.
- Vertical integration: Chinese companies often control the entire supply chain, from mining to processing and refining, reinforcing their market dominance.
Statistics reveal China's overwhelming market share, accounting for over 70% of global REE production and processing. This concentration creates a significant bottleneck, leaving Tesla, and other robotics companies, heavily reliant on a single source. Furthermore, the environmental impact of REE mining and processing remains a major concern. Establishing ethical and sustainable practices outside China presents significant challenges.
Geopolitical Risks and Supply Chain Vulnerability
Tesla's reliance on Chinese REEs exposes the Optimus project to substantial geopolitical risks and supply chain vulnerabilities.
The Risk of Trade Disputes and Sanctions
Escalating trade tensions or the imposition of sanctions on China could severely disrupt the flow of REEs to Tesla. Historical examples, such as past trade disputes impacting other commodity markets, demonstrate the potential for significant disruptions.
- Potential for export restrictions: China could restrict exports of REEs, creating shortages and driving up prices.
- Disruption of supply chains: Sanctions could lead to logistical bottlenecks and delays in the delivery of essential components.
Diversifying sourcing strategies is crucial, but it faces significant challenges, including the high capital costs involved in establishing new mining and processing facilities and the lack of readily available alternatives with equivalent technological maturity.
The Impact of Price Volatility
China's control over the REE supply allows it to influence prices, leading to significant volatility. This volatility directly impacts Tesla's manufacturing costs and profitability.
- Unpredictable pricing: Fluctuations in REE prices can make it challenging for Tesla to accurately forecast its manufacturing costs and set competitive prices for Optimus.
- Production planning challenges: Price volatility necessitates constant adjustments to production planning, potentially disrupting timelines and impacting efficiency.
Historical data shows significant price swings in key REEs, highlighting the risk of unpredictable costs for Tesla.
Tesla's Strategies to Mitigate Risk
To mitigate the risks associated with its reliance on Chinese REEs, Tesla needs to adopt a multifaceted strategy focusing on supply chain diversification and technological innovation.
Diversification of Suppliers
Tesla is likely pursuing strategies to diversify its supply chain beyond China, seeking alternative sources of REEs and partnering with companies in other countries. While specific details of these partnerships remain largely confidential, the task is monumental due to the significant technological and infrastructural hurdles involved in establishing viable alternatives.
- Exploration of new sources: Identifying and securing reliable supplies of REEs from other countries requires significant investment and long-term commitments.
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborating with mining and processing companies outside China can help secure access to crucial raw materials.
The feasibility of full diversification in the short-to-medium term remains questionable, given China's current market dominance.
Investment in Recycling and Material Substitution
Tesla's long-term strategy should also include significant investments in recycling rare earth materials and exploring alternative materials to reduce its dependence on REEs.
- Recycling initiatives: Developing advanced recycling technologies to recover REEs from end-of-life products could significantly reduce reliance on primary mining.
- Material substitution: Investing in research and development to identify and implement suitable alternative materials that can perform similar functions without the need for REEs would represent a significant breakthrough.
While these options present technological and economic challenges, they are crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability and security of Tesla’s robotics endeavors.
Conclusion
Tesla's Optimus project presents a significant technological leap, but its reliance on China's dominant rare earth supply chain poses a considerable threat. Geopolitical risks, price volatility, and supply chain vulnerabilities are major concerns. While Tesla is likely pursuing strategies to mitigate these risks, the long-term success of the Optimus project hinges on effectively diversifying its rare earth supply, investing in recycling technologies, and exploring alternative materials. Failing to address these rare earth supply chain challenges could severely impact the viability and timeline of this ambitious undertaking. A robust, multifaceted approach is essential to ensure the future of Tesla's Optimus robot and reduce its dependence on China's dominance in rare earth mineral production and processing.

Featured Posts
-
 Middle East Lpg Chinas Response To Us Tariff Hikes On Lpg Imports
Apr 24, 2025
Middle East Lpg Chinas Response To Us Tariff Hikes On Lpg Imports
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Analyzing Growth Mapping The Countrys Key Business Areas
Apr 24, 2025
Analyzing Growth Mapping The Countrys Key Business Areas
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Sk Hynix Leading The Dram Market With Ai Powered Innovation
Apr 24, 2025
Sk Hynix Leading The Dram Market With Ai Powered Innovation
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Us Lawyers Face Judge Abrego Garcias Crackdown On Stonewalling
Apr 24, 2025
Us Lawyers Face Judge Abrego Garcias Crackdown On Stonewalling
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Unconventional Approach How A Startup Airline Leverages Deportation Flights
Apr 24, 2025
Unconventional Approach How A Startup Airline Leverages Deportation Flights
Apr 24, 2025
