When Professionals Sell, Individuals Buy: Understanding Market Volatility
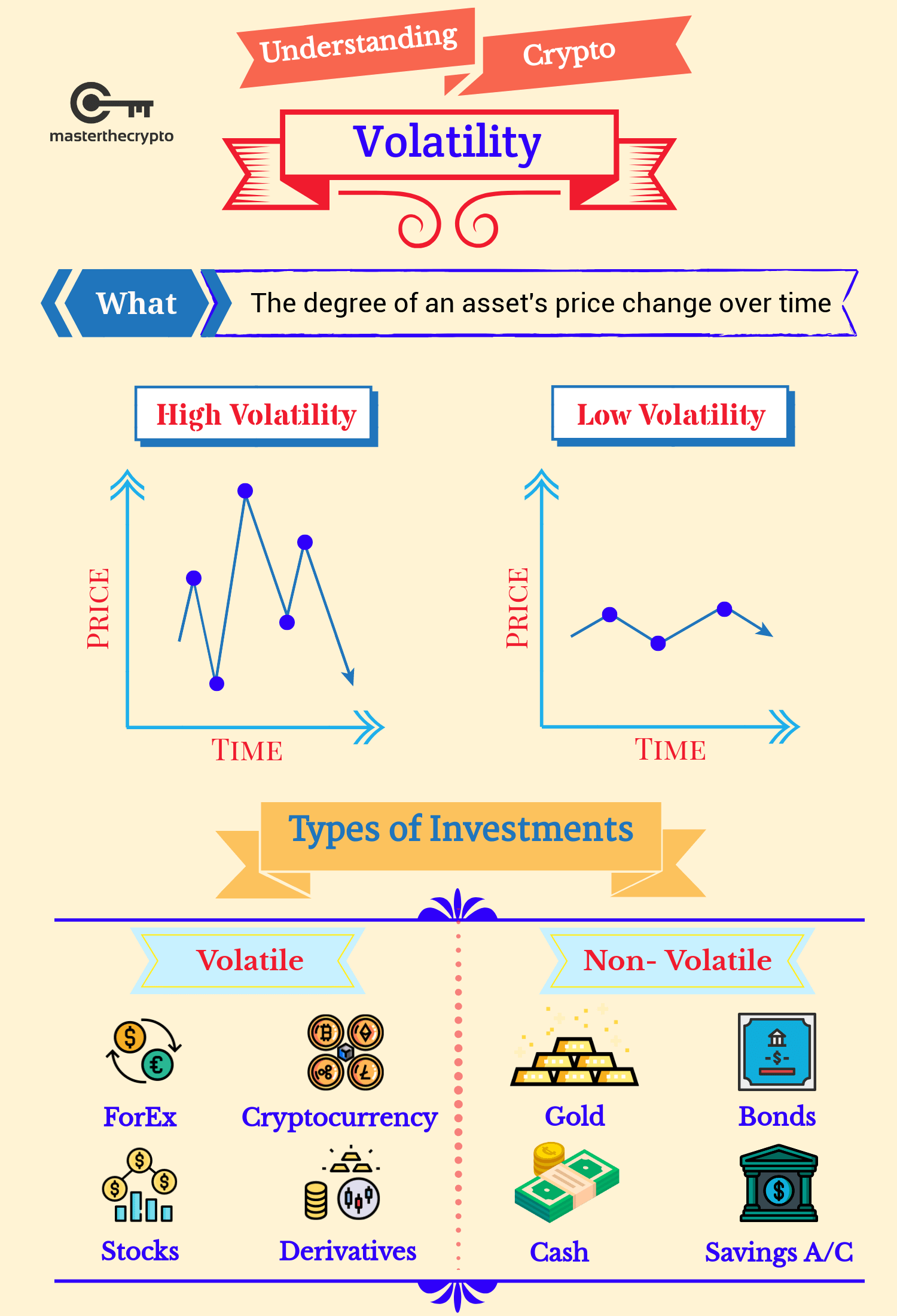
Table of Contents
Identifying the Signs of Market Volatility
Market volatility isn't simply a feeling; it's reflected in various measurable indicators and observable behavioral patterns. Understanding these signals is critical for preparing your investment strategy.
Understanding Market Indicators
Economic indicators provide a valuable glimpse into the health of the economy and, consequently, the potential for market volatility. Key indicators include:
- Inflation rates: High inflation often leads to increased interest rates and can trigger market uncertainty.
- Interest rates: Changes in interest rates directly impact borrowing costs and investment returns, influencing market sentiment.
- Unemployment figures: High unemployment suggests a weakening economy, potentially leading to market downturns.
Beyond macroeconomic factors, technical analysis tools help identify volatility patterns. These include:
- Moving averages: These smooth out price fluctuations to identify trends and potential reversals.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): This indicator helps measure the momentum of price changes, signaling overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This shows the relationship between two moving averages, highlighting potential trend changes.
Fundamental analysis is equally crucial. This involves evaluating the intrinsic value of assets, enabling investors to make informed decisions even during periods of high market volatility.
- Leading indicators of market volatility: Changes in consumer confidence, manufacturing activity, and bond yields.
- Lagging indicators of market volatility: Changes in unemployment rates, inflation rates, and corporate earnings.
- Different types of charts used to visualize market volatility: Candlestick charts (displaying open, high, low, and closing prices), line charts (showing price changes over time), and bar charts (representing price ranges).
Recognizing Behavioral Patterns
Market volatility is often amplified by investor behavior. Understanding these patterns is vital for mitigating risk.
-
Herd behavior: Investors often mimic each other's actions, leading to amplified price swings—buy high, sell low scenarios.
-
Fear and greed: These emotions drive irrational decision-making. Fear can lead to panic selling, while greed can lead to chasing unsustainable market trends.
-
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): This powerful emotion pushes investors into risky decisions, ignoring fundamental analysis.
-
Common emotional responses to market volatility: Anxiety, panic, euphoria, regret.
-
Strategies to mitigate emotional decision-making during volatile markets: Develop a well-defined investment plan, stick to your strategy, and seek professional financial advice.
Professional vs. Individual Investor Behavior During Volatility
The contrast between professional and individual investor behavior during periods of market volatility is striking.
Professional Investor Strategies
Professionals employ sophisticated strategies to navigate market volatility:
-
Hedging: Using financial instruments like options and futures to mitigate potential losses.
-
Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple asset classes and geographic regions to reduce overall risk.
-
Risk management: Employing rigorous risk assessment models and adjusting portfolios based on market conditions.
-
Access to resources: Professionals have access to advanced data analytics, research, and sophisticated trading tools.
-
Long-term horizon: They typically have a longer-term investment perspective, allowing them to weather short-term fluctuations.
-
Examples of hedging strategies: Buying put options to protect against stock price declines, using futures contracts to lock in prices.
-
Types of diversification strategies: Allocating assets across stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments; geographic diversification by investing in different countries.
Individual Investor Pitfalls
Individual investors often fall prey to emotional decision-making during market downturns:
-
Panic selling: Selling assets at a loss due to fear, often exacerbating market declines.
-
Chasing short-term gains: Following market trends without proper research, leading to high-risk, low-reward investments.
-
Lack of a plan: Failing to have a well-defined investment plan increases susceptibility to emotional reactions.
-
Common emotional biases: Confirmation bias (seeking information confirming pre-existing beliefs), overconfidence bias, herd mentality.
-
Examples of poor investment choices made during periods of market volatility: Investing in highly speculative assets, making impulsive trades based on news headlines.
Strategies for Managing Market Volatility
Effectively managing market volatility requires a proactive and disciplined approach.
Building a Diversified Portfolio
Diversification is crucial for reducing risk:
-
Asset allocation: Distributing investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities) to reduce the impact of any single asset's performance.
-
Risk tolerance: Adjusting asset allocation based on your individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
-
Examples of asset classes and their relative risk levels: Stocks (high risk, high potential return), bonds (moderate risk, moderate return), real estate (moderate risk, moderate return).
-
Strategies to adjust asset allocation based on market conditions: Rebalancing your portfolio periodically to maintain your target asset allocation.
Long-Term Investment Approach
Focusing on the long term is critical for weathering market volatility:
-
Long-term goals: Maintaining a clear focus on long-term financial goals, rather than reacting to short-term market fluctuations.
-
Discipline: Sticking to your investment plan despite market uncertainty.
-
Dollar-cost averaging: Investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market price.
-
Value investing: Focusing on undervalued assets with long-term growth potential.
-
Advantages and disadvantages of different investment strategies: Dollar-cost averaging mitigates the risk of investing a large sum at a market peak, but may not maximize returns in a consistently rising market. Value investing requires in-depth research but can generate significant long-term returns.
-
Tips for maintaining emotional resilience during market downturns: Regularly review your investment plan, avoid frequent portfolio checking, and seek professional guidance when needed.
Mastering Market Volatility for Long-Term Success
The key takeaway is this: professional investors often approach market volatility with a long-term perspective and sophisticated risk management strategies, while individual investors frequently react emotionally. Understanding market indicators, recognizing behavioral patterns, and building a well-diversified portfolio with a long-term approach are essential for navigating market volatility effectively. Learn how to effectively manage market volatility and build a resilient investment portfolio. Start planning your strategy today!

Featured Posts
-
 Pace Of Rent Increases Slows In Metro Vancouver Housing Costs Remain High
Apr 28, 2025
Pace Of Rent Increases Slows In Metro Vancouver Housing Costs Remain High
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Us Iran Nuclear Negotiations A Summary Of The Latest Discussions
Apr 28, 2025
Us Iran Nuclear Negotiations A Summary Of The Latest Discussions
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Starbucks Unions Rejection Of Proposed Pay Increase Highlights Labor Dispute
Apr 28, 2025
Starbucks Unions Rejection Of Proposed Pay Increase Highlights Labor Dispute
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Hamas Leaders In Cairo For Ceasefire Talks Amid Trumps Gaza Comments
Apr 28, 2025
Hamas Leaders In Cairo For Ceasefire Talks Amid Trumps Gaza Comments
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Mlb Scores Twins Triumph Over Mets 6 3
Apr 28, 2025
Mlb Scores Twins Triumph Over Mets 6 3
Apr 28, 2025
