Understanding High Stock Market Valuations: A BofA Viewpoint
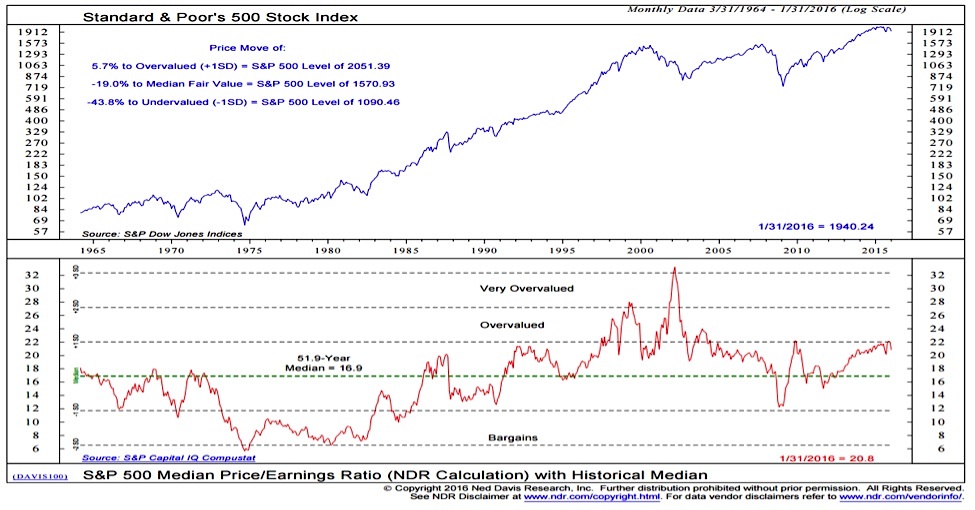
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics and Their Limitations
Understanding high stock market valuations requires analyzing various metrics. However, it's critical to recognize their limitations. Commonly used metrics include the Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E), Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S), and Price/Earnings to Growth ratio (PEG).
-
P/E Ratio: This classic metric compares a company's stock price to its earnings per share. While seemingly straightforward, a high P/E ratio might indicate either high growth expectations or an overvalued stock. Interest rate changes significantly impact P/E ratios; rising rates often lead to lower valuations. A low P/E ratio, conversely, might signal undervaluation or potential risk.
-
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S): Useful for evaluating companies with no earnings (e.g., startups), the P/S ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its revenue. However, it's crucial to consider industry-specific norms, as P/S ratios vary widely across sectors. A high P/S ratio might suggest high growth potential, but it can also mask underlying issues.
-
PEG Ratio: This metric attempts to account for growth by dividing the P/E ratio by the company's expected earnings growth rate. A PEG ratio below 1 is generally considered undervalued, while a ratio above 1 might suggest overvaluation. However, accurately predicting future growth is inherently challenging, limiting the PEG ratio's predictive power.
(Insert chart here illustrating historical trends of P/E, P/S, and PEG ratios for a major index like the S&P 500.)
Macroeconomic Factors Influencing High Stock Market Valuations
Several macroeconomic factors contribute to high stock market valuations. Low interest rates, for example, significantly influence asset prices. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, increasing investment and potentially inflating asset bubbles.
-
Impact of Quantitative Easing (QE): Central banks' QE programs inject liquidity into the market, driving up asset prices, including stocks. This can contribute to inflated valuations.
-
Inflation's Effect: High inflation erodes purchasing power and can impact corporate earnings, potentially leading to lower stock valuations. Conversely, controlled inflation can be positive for growth.
-
Geopolitical Risks: Uncertainties stemming from geopolitical events, such as trade wars or international conflicts, can create market volatility and affect stock valuations. These events introduce risk premiums into market pricing.
(Include relevant data and statistics from BofA research to support the above points. For example, cite BofA's forecasts for interest rate changes and their predicted impact on market valuations.)
Assessing the Risks of High Stock Market Valuations
High stock market valuations inherently carry risks. History shows that periods of inflated valuations are often followed by market corrections or even crashes.
-
Historical Precedents: Examining historical market cycles reveals that extended periods of high valuations frequently precede significant market downturns. The dot-com bubble of the late 1990s and the housing bubble of the mid-2000s serve as stark reminders.
-
Identifying Bubbles: While pinpointing bubbles precisely is impossible, signs such as rapidly rising prices, excessive speculation, and widespread investor euphoria often signal potential overvaluation.
-
Risk Management Strategies: Diversification across asset classes, sectors, and geographies is crucial for mitigating risk during periods of high valuations. Hedging strategies, such as using options or inverse ETFs, can also help manage downside risk.
BofA's Perspective on Navigating High Stock Market Valuations
BofA's analysts closely monitor macroeconomic conditions and valuation metrics. Our current outlook suggests a cautious approach to investing in the face of these high stock market valuations.
-
BofA's Investment Recommendations: (Insert BofA's specific recommendations here. For example: a focus on value stocks, specific sector preferences, and suggested asset allocation strategies.) This might involve a more conservative approach, emphasizing defensive sectors or diversifying into alternative assets.
-
Risk Management Strategies: BofA recommends a robust risk management framework, including stress testing portfolios against various market scenarios and regularly reviewing asset allocation to align with changing market conditions.
-
Investment Horizons: Maintaining a long-term investment horizon is crucial, allowing investors to weather short-term market fluctuations. However, understanding the current elevated valuations is key to formulating a prudent long-term strategy.
(Include quotes from BofA analysts to support the above points and lend authority.)
Conclusion: Understanding High Stock Market Valuations – A BofA Perspective
Understanding high stock market valuations is paramount for investors. We've explored key valuation metrics, their limitations, macroeconomic influences, and inherent risks. While growth potential exists, the current environment requires a cautious approach. BofA's perspective emphasizes a balanced strategy incorporating robust risk management and a clear understanding of your investment horizon. To develop a personalized investment strategy tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals in light of high stock market valuations, consult with a financial advisor. Explore BofA's comprehensive research and resources for further insights into navigating these challenging market conditions.

Featured Posts
-
 I Cant Believe Marvels Potential Jean Grey Casting Choice
Apr 25, 2025
I Cant Believe Marvels Potential Jean Grey Casting Choice
Apr 25, 2025 -
 The Dnieper River A Pathway To Peace
Apr 25, 2025
The Dnieper River A Pathway To Peace
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Nba Launches Formal Probe Into Ja Morant Incident
Apr 25, 2025
Nba Launches Formal Probe Into Ja Morant Incident
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Harvard And Foreign Funding Examining The Trump Administrations Scrutiny
Apr 25, 2025
Harvard And Foreign Funding Examining The Trump Administrations Scrutiny
Apr 25, 2025 -
 How To Watch Eurovision 2025 Live From Australia
Apr 25, 2025
How To Watch Eurovision 2025 Live From Australia
Apr 25, 2025
