The Continued Support Of European Shipyards In Russia's Arctic Gas Ambitions
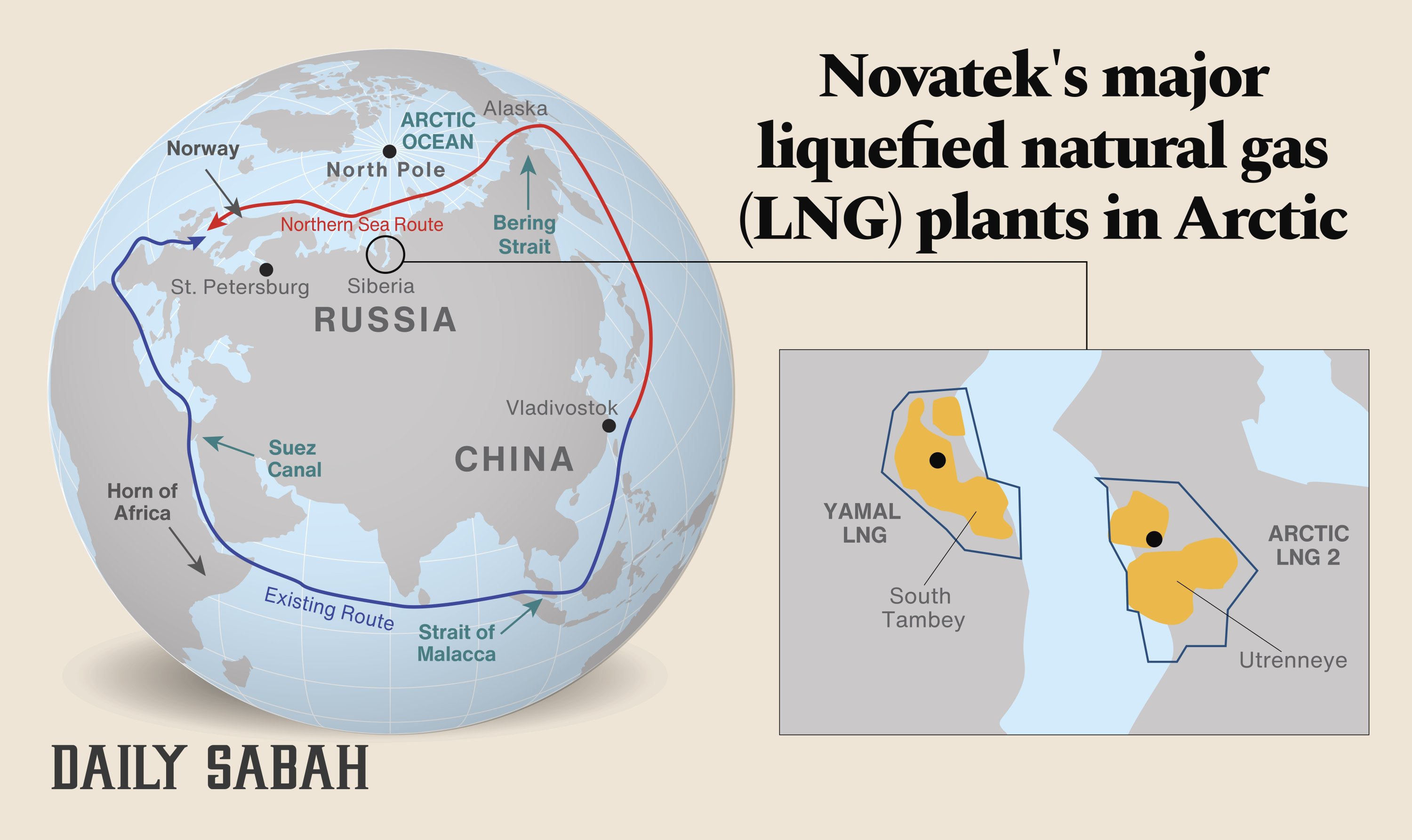
Table of Contents
The Crucial Role of Specialized Ice-Class Vessels
Operating in the Arctic's harsh environment demands specialized vessels capable of withstanding extreme ice conditions. The unique challenges – including thick ice formations, frigid temperatures, and unpredictable weather – necessitate robust ice-class vessels. These are not your average cargo ships; they require advanced engineering and construction techniques. Russia's Arctic gas extraction projects rely heavily on several key vessel types:
- LNG Carriers: Massive ships designed to transport liquefied natural gas (LNG) safely and efficiently through ice-infested waters.
- Icebreakers: Powerful vessels capable of breaking through thick ice to create navigable pathways for other ships.
- Supply Ships: Vessels responsible for delivering essential supplies, equipment, and personnel to remote Arctic operations.
Several European shipyards have played, and continue to play, a pivotal role in providing these specialized vessels.
- Examples: Finnish shipyards, known for their expertise in icebreaker technology, have built numerous ice-class vessels for Russian Arctic projects. Norwegian and Dutch yards have also contributed significantly to the construction of LNG carriers and supply ships designed for Arctic operations.
- Technical Specifications: These vessels often boast impressive icebreaking capacities, measured in terms of ice thickness they can navigate. Advanced cargo handling systems and robust hull designs are essential features, tailored to the demanding Arctic conditions. For example, some ice-class LNG carriers can handle ice thicknesses exceeding 2 meters.
Economic Incentives and Business Relationships
The contracts for building ice-class vessels represent lucrative business opportunities for European shipyards. These projects inject substantial capital into the European shipbuilding industry, supporting thousands of jobs across various countries. Long-standing business relationships between European and Russian companies have further fostered this collaboration.
- Financial Scale: Contracts for the construction of individual ice-class vessels can run into hundreds of millions of euros, representing substantial revenue streams for European shipyards.
- Potential Revenue Loss: The cessation of these contracts would have a significant negative impact on the financial performance of these shipyards, potentially leading to job losses and economic downturn in related sectors.
- Employment Impact: Thousands of highly skilled workers in European shipbuilding industries are directly and indirectly employed through these contracts. The loss of these contracts would pose a severe threat to their livelihoods.
Geopolitical Implications and Ethical Concerns
The continued support of European shipyards for Russia's Arctic energy development raises complex geopolitical and ethical questions. This collaboration contributes to Russia's energy independence, potentially enhancing its geopolitical influence.
- Sanctions and their Impact: International sanctions imposed on Russia may impact the ability of European companies to engage in these projects, creating uncertainty and potential legal complexities. The navigation of these sanctions is a significant hurdle for both sides.
- Environmental Consequences: The extraction and transportation of Arctic gas pose significant environmental risks, including the potential for oil spills and damage to fragile Arctic ecosystems. The carbon footprint of such projects also raises concerns about climate change.
- International Pressure: Growing international pressure to curb Arctic development due to environmental concerns and geopolitical tensions puts increasing pressure on European shipyards involved in these projects.
Future of European Shipyard Involvement
The future of European shipyard participation in Russia's Arctic projects remains uncertain. Geopolitical instability, evolving international regulations, and environmental concerns will significantly influence future decisions.
- Future Demand: The long-term demand for ice-class vessels in the Arctic will depend on several factors, including global energy demand, the development of alternative energy sources, and the success of sanctions imposed on Russia.
- Diversification Strategies: European shipyards are likely to explore diversification strategies to reduce their dependence on Russian contracts and mitigate geopolitical risks. This may involve focusing on other markets, such as offshore wind energy projects or the development of more sustainable shipping solutions.
- Alternative Markets and Sustainable Energy: The transition towards renewable energy sources offers an opportunity for European shipyards to diversify their activities and focus on technologies and infrastructure related to sustainable energy production and transportation.
Conclusion
The continued support of European shipyards in Russia's Arctic gas ambitions reveals a complex interplay of economic interests, geopolitical realities, and ethical considerations. While the economic benefits for European shipyards are undeniable, the environmental and geopolitical risks associated with contributing to Russia's Arctic energy development cannot be ignored. Further research and discussion are crucial to fully understand the long-term implications of European shipyards and Russia's Arctic gas ambitions. We need a comprehensive strategy to navigate this intricate relationship responsibly, balancing economic necessities with ethical and environmental concerns.

Featured Posts
-
 Why Middle Managers Are Crucial For Company Success And Employee Well Being
Apr 26, 2025
Why Middle Managers Are Crucial For Company Success And Employee Well Being
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Increased Birth Control Access Examining The Post Roe Otc Landscape
Apr 26, 2025
Increased Birth Control Access Examining The Post Roe Otc Landscape
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Andrew Cuomo And Chelsea Handler A Date That Never Happened And Why
Apr 26, 2025
Andrew Cuomo And Chelsea Handler A Date That Never Happened And Why
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Potential Us Thailand Tariff Agreement Thaksins Role And Policy Changes
Apr 26, 2025
Potential Us Thailand Tariff Agreement Thaksins Role And Policy Changes
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Us China Rivalry A Key Military Base In The Crosshairs
Apr 26, 2025
Us China Rivalry A Key Military Base In The Crosshairs
Apr 26, 2025
