Tesla's Optimus Robot: China's Rare Earth Restrictions Cause Delays
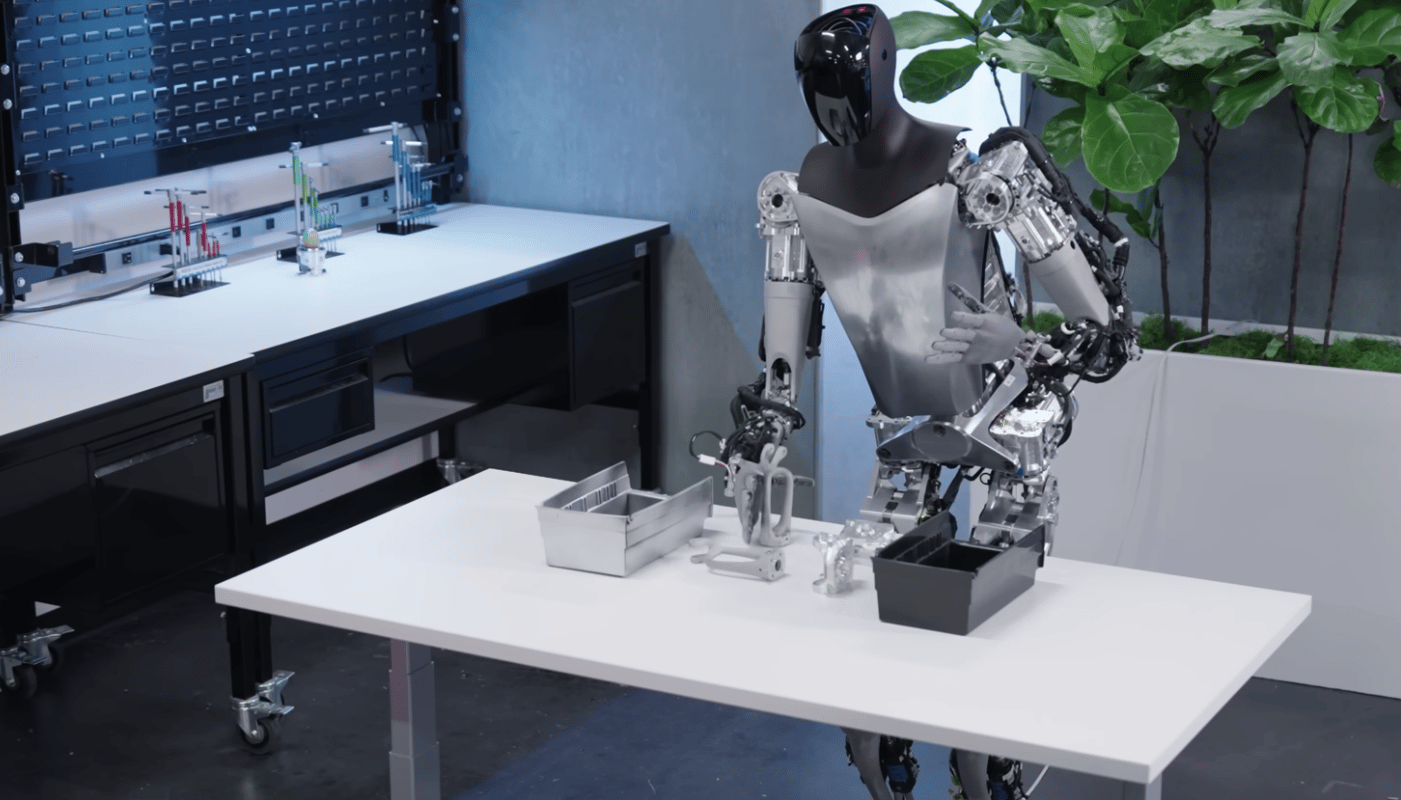
Table of Contents
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Minerals and its Geopolitical Implications
China holds a near-monopoly on the mining and processing of rare earth elements (REEs), controlling approximately 60-70% of global production. These minerals, though found globally, require complex and environmentally intensive processing, a domain where China has established a significant advantage. This dominance extends far beyond simply controlling the supply; it has significant geopolitical implications. Rare earth minerals are critical components in a vast array of advanced technologies, from smartphones and wind turbines to electric vehicles and, crucially, sophisticated robots like Tesla's Optimus.
The US and other nations are increasingly concerned about this dependence. The concentration of power over these essential materials presents significant vulnerabilities in global supply chains and technological advancement.
- Percentage of global rare earth production controlled by China: 60-70%
- Specific rare earth elements crucial for Optimus robot's components: Neodymium (Nd), Dysprosium (Dy), Praseodymium (Pr) – vital for powerful, lightweight motors and advanced sensors.
- Examples of other technologies impacted by China's rare earth control: Electric vehicles, wind turbines, aerospace components, medical imaging equipment.
The Specific Rare Earth Needs of Tesla's Optimus Robot
Tesla's Optimus robot relies heavily on rare earth minerals for its functionality. These minerals are not just used for show; they are integral to the robot's performance. The sophisticated motors that enable Optimus's movement require neodymium magnets for their high power-to-weight ratio. Similarly, various sensors and actuators utilize rare earth materials for their sensitivity and precision. The quantity of these materials needed for mass production is substantial, making Tesla significantly vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
- Specific components requiring rare earth minerals: Motors, sensors, actuators, control systems.
- Potential alternatives (if any) and their limitations: While research into alternative materials is ongoing, current substitutes often lack the performance characteristics of rare earth elements, resulting in less efficient or less powerful robots.
- Technological challenges in substituting rare earth materials: Developing and scaling up production of viable alternatives is a complex and time-consuming process, facing significant technological and economic hurdles.
How Rare Earth Restrictions Directly Impact Optimus Robot Production
China's potential export controls or restrictions on rare earth minerals directly impact Tesla's ability to produce the Optimus robot at scale. These restrictions, whether through quotas, tariffs, or other regulatory measures, create significant bottlenecks in Tesla's supply chain. This results in delays in manufacturing, pushing back Tesla's ambitious timeline for Optimus's market rollout. The financial implications are substantial, impacting not only production costs but also potentially delaying the revenue generation anticipated from Optimus sales.
- Types of restrictions imposed by China (quotas, tariffs, etc.): While not explicitly targeting Tesla, broader restrictions on rare earth exports could severely impact supply.
- The impact on the production timeline for Optimus: Delays are already being reported, and further restrictions could significantly extend the time to market.
- Potential cost increases for Tesla due to supply chain issues: Increased prices for rare earth minerals inevitably translate to higher production costs for the Optimus robot.
Tesla's Strategies to Mitigate Rare Earth Dependence
To mitigate its dependence on Chinese rare earth minerals, Tesla is likely pursuing several strategies. This might involve diversifying its sourcing to include suppliers from other countries like Australia, Vietnam, or the US, even if those sources currently produce smaller quantities. Tesla might also be investing heavily in research and development to find viable substitutes for rare earth materials in its robot's components. Additionally, direct investment in rare earth mining and processing outside China could offer long-term supply security.
- Potential alternative suppliers of rare earth minerals: Australia, Vietnam, Brazil, Canada, and the US are all exploring ways to increase their rare earth production.
- Research and development efforts to find rare earth substitutes: This is a critical area of ongoing research in materials science, though breakthroughs remain a long-term prospect.
- Investment in domestic rare earth mining and processing: This is a long-term solution requiring significant capital investment and potentially overcoming environmental regulations.
Conclusion: Navigating the Challenges – The Future of Tesla's Optimus Robot
Tesla's Optimus robot faces significant challenges due to China's dominant position in the rare earth minerals market. The reliance on these minerals for critical components highlights the vulnerability of advanced robotics to geopolitical factors. The long-term implications for Tesla and the broader robotics industry are significant, necessitating diversification efforts and innovative solutions. The future of Optimus hinges on Tesla's success in navigating this complex landscape and securing a reliable supply chain for crucial rare earth materials. Learn more about the future of Tesla's Optimus robot and its challenges by following the latest updates on rare earth restrictions and their impact on robotics.

Featured Posts
-
 Blue Origin Cancels Launch Vehicle Subsystem Issue Delays Mission
Apr 24, 2025
Blue Origin Cancels Launch Vehicle Subsystem Issue Delays Mission
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Od Djevojcice Do Ljepotice Pogledajte Kako Je Ella Travolta Izrasla
Apr 24, 2025
Od Djevojcice Do Ljepotice Pogledajte Kako Je Ella Travolta Izrasla
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 24, 2025
Bmw And Porsches China Challenges A Growing Trend In The Auto Industry
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Stonewalling Tactics Condemned Judge Abrego Garcias Ruling Impacts Us Legal Cases
Apr 24, 2025
Stonewalling Tactics Condemned Judge Abrego Garcias Ruling Impacts Us Legal Cases
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Elite Universities Under Pressure A Funding Fight
Apr 24, 2025
Elite Universities Under Pressure A Funding Fight
Apr 24, 2025
