Over-the-Counter Birth Control: Implications For Reproductive Rights After Roe V. Wade

Table of Contents
Increased Access and Reduced Barriers
The availability of over-the-counter birth control has the potential to dramatically improve access to contraception, particularly for those currently facing significant barriers.
Geographic Barriers
Access to reproductive healthcare varies drastically across the US. Many rural and underserved communities face significant challenges in obtaining birth control, including:
- Limited number of clinics: Sparsely populated areas often lack the necessary healthcare infrastructure.
- Long travel distances: Reaching the nearest clinic can require extensive travel, creating both time and financial burdens.
- Lack of transportation: Reliable transportation is not always available, especially for those without personal vehicles.
- High cost of care: Even with insurance, transportation and time off work can add significant expense to obtaining birth control.
Financial Barriers
The cost of prescription birth control, including doctor visits and medication, represents a substantial financial burden for many, especially low-income individuals and families:
- Cost of doctor visits: Regular check-ups and consultations add to the overall expense.
- Prescription costs: The price of birth control pills, patches, rings, and other methods can be prohibitive.
- Insurance coverage limitations: Many insurance plans have limitations on contraceptive coverage, leaving individuals with significant out-of-pocket costs.
Time Barriers
Obtaining prescription birth control requires a significant time commitment:
- Appointment scheduling difficulties: Scheduling appointments with healthcare providers can be challenging, particularly with limited availability.
- Waiting times at clinics: Long waiting times at clinics further add to the inconvenience.
- Potential delays in filling prescriptions: Delays in obtaining prescriptions can disrupt consistent use and reduce effectiveness.
Stigma and Shame
Social stigma surrounding birth control can deter individuals from seeking necessary care:
- Fear of judgment from healthcare providers: Concerns about judgment or lack of understanding from healthcare professionals can be a significant deterrent.
- Concerns about privacy: Privacy concerns can prevent individuals from seeking help.
- Cultural or religious beliefs: Cultural or religious beliefs may influence attitudes towards contraception and access to services.
Potential for Increased Rates of Contraceptive Use
Increased accessibility of over-the-counter birth control could have profound effects on contraceptive use rates and public health.
Convenience and Accessibility
Easier access to birth control could significantly increase rates of contraceptive use:
- Increased convenience of purchase: The ability to purchase birth control at drugstores or online offers unparalleled convenience.
- Easier integration into daily routines: Convenient access allows for easier integration of birth control into daily routines, increasing adherence.
- Reduced barriers to consistent use: Removing barriers to access encourages consistent use, leading to higher effectiveness.
Improved Public Health Outcomes
Widespread use of contraception leads to positive public health outcomes:
- Lower abortion rates: Increased access to effective contraception directly reduces unintended pregnancies and consequently, the need for abortions.
- Reduced incidence of STIs: Increased contraceptive use can also reduce the spread of sexually transmitted infections.
- Improved maternal health: Access to contraception allows for better family planning, leading to improved maternal and child health outcomes.
Impact on Maternal Mortality
Improved access to birth control can significantly reduce maternal mortality rates:
- Prevention of high-risk pregnancies: Access to contraception helps prevent high-risk pregnancies associated with unintended pregnancies.
- Decreased need for unsafe abortions: Reduced need for abortions, especially unsafe ones, directly reduces mortality risk.
- Improved access to prenatal care: Better family planning enables improved access to prenatal care and monitoring.
Potential Challenges and Concerns
While the benefits of over-the-counter birth control are significant, potential challenges must be addressed.
Misinformation and Misuse
The increased accessibility of over-the-counter birth control necessitates robust education campaigns to combat misinformation:
- Lack of proper education on usage: Individuals may lack adequate understanding of proper usage and potential side effects.
- Potential for incorrect dosage or timing: Incorrect use can significantly reduce effectiveness.
- Reliance on unreliable sources of information: The proliferation of misinformation online necessitates reliable sources of information.
Lack of Medical Oversight
Removing medical oversight raises concerns regarding healthcare:
- Limited opportunity for comprehensive sexual health education and counseling: Regular consultations with healthcare providers offer valuable educational opportunities and counseling.
- Lack of screening for other health conditions: Doctor visits offer opportunities for screenings for other health conditions.
- Difficulty managing side effects: Medical professionals are essential in managing potential side effects and complications.
Political Opposition
The political landscape surrounding reproductive rights presents challenges to increased access:
- Legislative challenges at state and federal levels: State-level restrictions and potential future legislative challenges pose threats to access.
- Restrictions on advertising and promotion: Restrictions on advertising and promotion could limit awareness and access.
- Potential for future legal challenges: Legal challenges to the availability of over-the-counter birth control remain a possibility.
Conclusion
The shift towards over-the-counter birth control offers a significant opportunity to improve access to reproductive healthcare and empower individuals to make informed choices about their bodies. While increased convenience and accessibility could lead to improved public health outcomes, careful consideration must be given to potential challenges, including the risks of misinformation and the need for comprehensive education and support. The future of reproductive rights in a post-Roe world hinges on ensuring equitable access to all forms of contraception. Advocating for increased access to affordable and readily available over-the-counter birth control, including increased education and support, remains crucial in protecting reproductive freedom for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Gambling On Natural Disasters The Troubling Trend Of La Wildfire Bets
Apr 22, 2025
Gambling On Natural Disasters The Troubling Trend Of La Wildfire Bets
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Mapping The Countrys Newest Business Hubs
Apr 22, 2025
Mapping The Countrys Newest Business Hubs
Apr 22, 2025 -
 1 Billion More Trump Administration Deepens Funding Cuts To Harvard
Apr 22, 2025
1 Billion More Trump Administration Deepens Funding Cuts To Harvard
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Razer Blade 16 2025 Review Ultra Settings On A Thin Laptop The Price Is Steep
Apr 22, 2025
Razer Blade 16 2025 Review Ultra Settings On A Thin Laptop The Price Is Steep
Apr 22, 2025 -
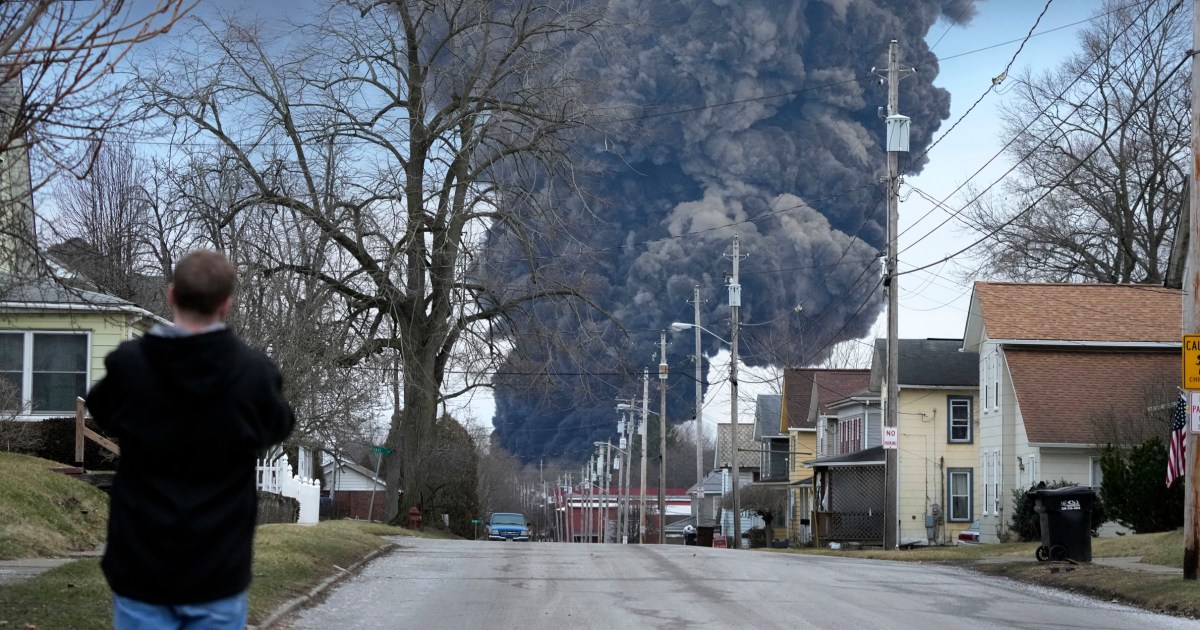 Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Months Long Impact On Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Months Long Impact On Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
