Liberal Fiscal Policies: A Critical Analysis
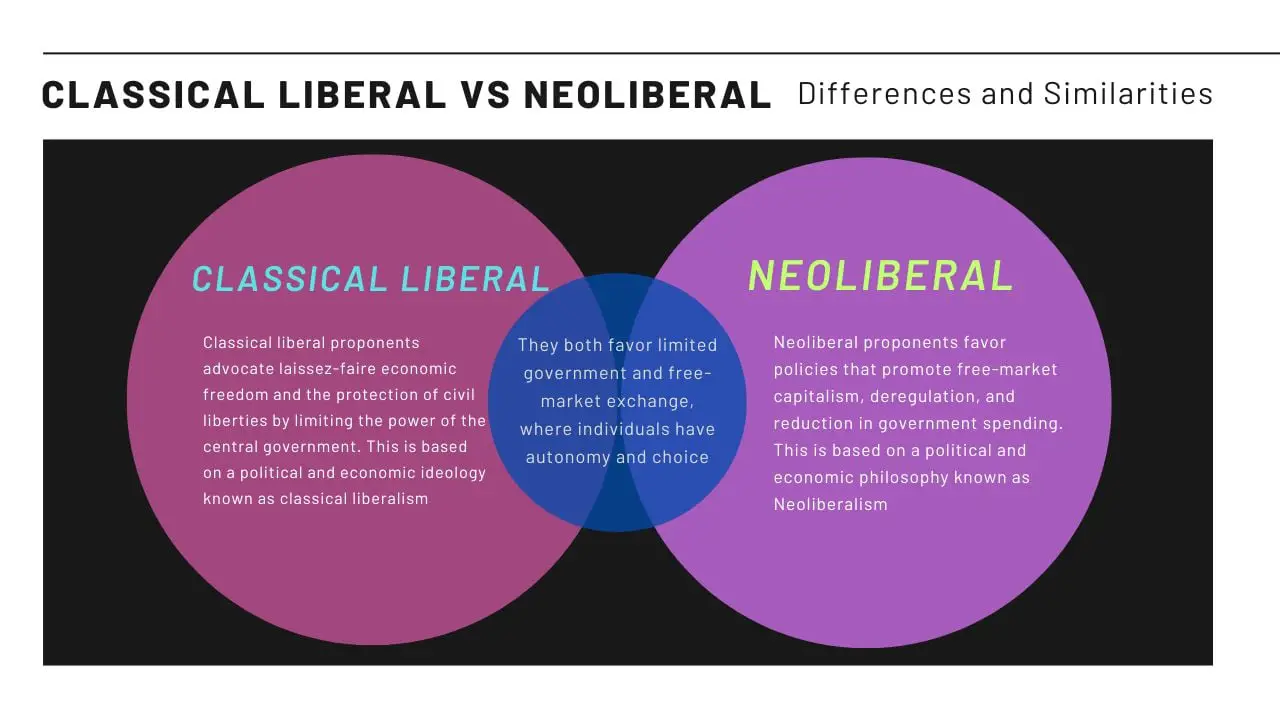
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Liberal Fiscal Policies and Their Impact
Liberal fiscal policies are characterized by a proactive government role in managing the economy through active government spending, strategic taxation policies, and often, the acceptance of budget deficits. These policies prioritize economic stimulus and the expansion of social welfare programs to address societal needs and promote equitable growth. They stand in contrast to more conservative approaches emphasizing fiscal austerity and limited government intervention. This analysis will focus on the impact of these policies across various economic contexts and historical periods.
2. Main Points:
H2: Key Features of Liberal Fiscal Policies:
Liberal fiscal policies are defined by several core elements. They typically involve a progressive tax system, where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. This revenue is then channeled into increased social welfare spending, encompassing areas such as healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits. Furthermore, governments adopting these policies often invest heavily in public goods, including infrastructure projects designed to boost long-term economic productivity. This signifies an active role in managing the economy through targeted fiscal tools.
- Progressive tax system: Higher earners pay a proportionally higher tax rate.
- Increased social welfare spending: Expanded safety nets and public services.
- Government investment in public goods: Infrastructure development and other public projects.
- Active role in managing the economy: Using fiscal policy to influence economic activity.
Examples of countries that have implemented, to varying degrees, policies consistent with this model include the Nordic countries (Sweden, Denmark, Norway), Canada, and, at certain times, the United States.
H2: Economic Impacts of Liberal Fiscal Policies: The Arguments For and Against:
H3: Arguments in Favor:
Proponents of liberal fiscal policies argue they lead to several positive outcomes. Increased government spending can boost aggregate demand, stimulating economic growth and creating jobs. Progressive taxation can reduce income inequality, fostering a more equitable distribution of wealth. Investments in education and healthcare improve human capital, further enhancing long-term productivity. These arguments find theoretical grounding in Keynesian economics, which emphasizes the government's role in stabilizing the economy during periods of recession. Empirical evidence from various countries suggests a correlation between social spending and improved health and education outcomes.
H3: Arguments Against:
Critics of liberal fiscal policies raise concerns about their potential drawbacks. Increased government spending can lead to larger government debt, potentially jeopardizing fiscal sustainability. Large-scale government borrowing can also lead to the crowding out effect, where increased government demand for funds pushes up interest rates, hindering private investment. Furthermore, concerns exist about the potential for inflation and government inefficiency in spending programs. These arguments align with alternative economic perspectives, such as Austrian or supply-side economics, that emphasize the importance of limited government intervention and market forces.
H2: Case Studies: Examining Real-World Examples of Liberal Fiscal Policies:
The implementation of liberal fiscal policies has yielded varied results across different countries and historical periods. For example, the post-war economic boom in several Western European countries is often cited as evidence of the success of such policies. Conversely, some argue that the high levels of government debt in certain countries are a direct result of these policies. Analyzing specific case studies, including detailed examination of economic performance indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and changes in income inequality, provides crucial empirical evidence for evaluating their effectiveness. This needs careful contextualization, acknowledging differing initial conditions and external factors.
- Case Study 1: The Nordic model – Analyzing the impact on social welfare and economic growth.
- Case Study 2: Post-war Western Europe – Examining the role of government spending in economic recovery.
- Case Study 3: Specific policy interventions like the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 – Assessing effectiveness and limitations.
H2: Challenges and Limitations of Liberal Fiscal Policies:
Implementing and maintaining liberal fiscal policies faces significant challenges. Political feasibility is a major hurdle, as these policies often require broad political consensus and may face resistance from groups advocating for lower taxes and reduced government spending. Bureaucratic inefficiencies can hinder effective policy implementation, leading to wasted resources and reduced impact. Careful policy design is crucial to ensure that programs are targeted, effective, and achieve their intended goals. Finally, ensuring fiscal sustainability in the long run is paramount, as unchecked increases in government debt can have severe consequences.
3. Conclusion: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Liberal Fiscal Policies – A Call to Action
Liberal fiscal policies present a complex picture, with both compelling arguments in their favor and significant potential drawbacks. Their effectiveness depends heavily on various factors, including the specific context, the design and implementation of the policies, and the broader economic environment. While they can contribute to reduced inequality and economic stimulus, careful consideration of potential risks like increased government debt and inflation is crucial. Further research, data-driven policymaking, and ongoing critical evaluation of liberal fiscal policies in diverse contexts are essential to fully understand their long-term consequences. We encourage readers to delve deeper into this subject through further reading and participation in relevant discussions to foster a more informed understanding of these crucial economic strategies.

Featured Posts
-
 Office365 Data Breach Crook Makes Millions Federal Investigation Reveals
Apr 24, 2025
Office365 Data Breach Crook Makes Millions Federal Investigation Reveals
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Trump Administration Immigration Crackdown Legal Challenges Mount
Apr 24, 2025
Trump Administration Immigration Crackdown Legal Challenges Mount
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Double Strike In Hollywood What It Means For Film And Television
Apr 24, 2025
Double Strike In Hollywood What It Means For Film And Television
Apr 24, 2025 -
 The Business Of Deportation How One Startup Airline Is Making It Work
Apr 24, 2025
The Business Of Deportation How One Startup Airline Is Making It Work
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting And Its Implications
Apr 24, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting And Its Implications
Apr 24, 2025
