China's Emissions Reduction: Xi's Pledge At International Climate Talks
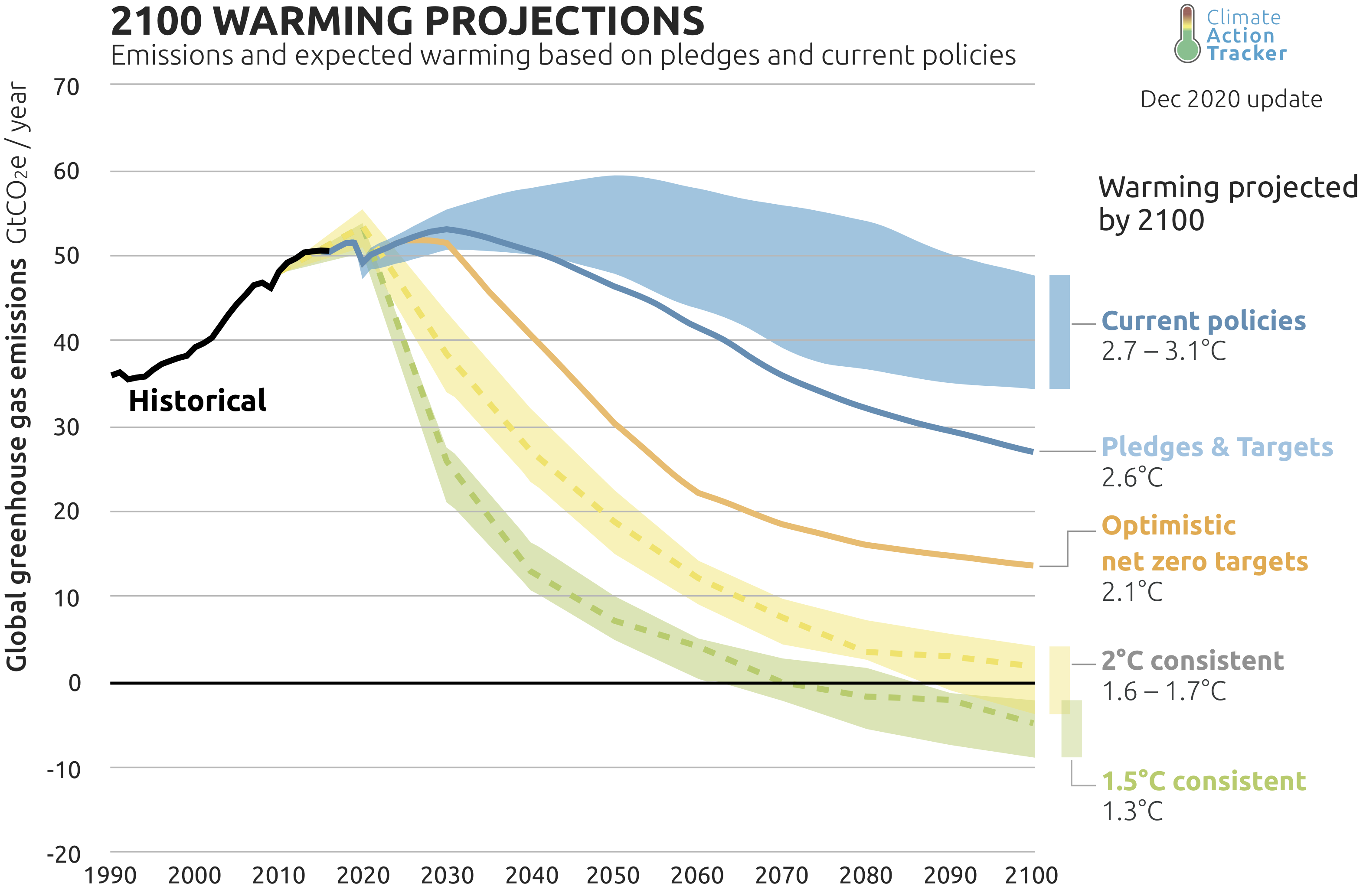
Table of Contents
Xi Jinping's Key Commitments at International Climate Talks
The COP27 Pledge and Beyond
At COP27, and in subsequent statements, Xi Jinping reiterated China's commitment to peaking carbon emissions before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality before 2060. While specific, detailed plans were not unveiled at COP27 itself, these overarching targets represent a monumental undertaking.
- Specific Numerical Targets: The pledge includes peaking carbon dioxide emissions before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality before 2060. This implies a drastic reduction in reliance on fossil fuels and a massive expansion of renewable energy sources.
- Policy Initiatives: Alongside these targets, China has emphasized investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including solar, wind, and hydropower. Further initiatives focus on improving energy efficiency across various sectors and promoting sustainable development practices.
- Official Sources: These commitments are documented in official statements released by the Chinese government and reported by international news agencies like Xinhua and Reuters. Verification of progress against these targets relies on ongoing data collection and analysis.
Previous Commitments and Progress
China's commitment to emissions reduction isn't new. Previous pledges, often made at previous COP meetings and within national policy documents, provide a backdrop against which to assess recent progress.
- Previous Commitments and Outcomes: Past commitments included targets for increasing the share of renewable energy in the national energy mix and reducing energy intensity (energy consumption per unit of GDP). While some progress has been made, meeting these earlier targets hasn't always been straightforward.
- Factors Influencing Success/Setbacks: Economic growth, technological limitations, and the sheer scale of the challenge have all contributed to both successes and setbacks in achieving prior emissions reduction goals. The rapid industrialization of certain regions has, for instance, presented ongoing obstacles.
- Emissions Trends and Policy Correlation: Data from sources like the Global Carbon Project show a complex picture. While China has made strides in reducing its carbon intensity (emissions per unit of GDP), absolute emissions have continued to rise, highlighting the scale of the challenge. The correlation between specific policy implementations and actual emission reductions remains a subject of ongoing research and debate.
Challenges in Achieving China's Emissions Reduction Goals
Economic Growth vs. Environmental Protection
China's economic growth has been fueled, in part, by heavy reliance on coal-fired power plants. Reconciling the need for continued economic development with the imperative of emissions reduction presents a major hurdle.
- High-Carbon Footprint Sectors: Industries like steel, cement, and heavy manufacturing contribute significantly to China's carbon footprint. Transitioning these sectors to cleaner technologies requires substantial investment and innovation.
- Coal Phase-Out Challenges: Reducing reliance on coal, a dominant energy source in China, is a complex undertaking. It requires diversification of energy sources, development of alternative energy infrastructure, and careful management of potential social and economic disruptions in coal-producing regions.
- Balancing Economic Development and Sustainability: Strategies for balancing these competing needs include promoting green technologies, investing in renewable energy infrastructure, and implementing carbon pricing mechanisms. However, implementing these strategies effectively requires careful planning and execution.
Technological Innovation and Infrastructure
Achieving ambitious emissions reduction targets demands significant advancements in technology and substantial investments in new infrastructure.
- Key Technological Advancements: This includes breakthroughs in renewable energy technologies (e.g., more efficient solar panels, advanced wind turbines), carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, and smart grids for efficient energy distribution.
- Infrastructure Investment Scale: Building the necessary infrastructure to support a transition to a low-carbon economy requires massive investment in renewable energy power plants, transmission lines, and smart grids.
- International Collaboration: International collaboration will be crucial in facilitating technology transfer, sharing best practices, and securing financing for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Policy Implementation and Enforcement
Effective implementation and enforcement of environmental policies are vital to driving meaningful emissions reductions.
- Strengths and Weaknesses of Current Policies: China has implemented various environmental policies, including emissions trading schemes and renewable energy targets. However, challenges remain in terms of consistent enforcement, addressing loopholes, and ensuring compliance across all levels of government.
- Improvements to Policy Implementation: Strengthening enforcement mechanisms, enhancing transparency, and improving data collection and reporting are crucial steps toward more effective implementation.
- Role of Local Governments and Public Participation: Engaging local governments and promoting public awareness and participation are vital to fostering a sense of shared responsibility and ensuring broad-based support for emissions reduction efforts.
Conclusion
Xi Jinping's pledges on China's emissions reduction represent a significant commitment to global climate action. The targets are ambitious, acknowledging the need for substantial change. However, achieving these goals faces significant challenges, including balancing economic growth with environmental protection, investing in technological innovation, and ensuring effective policy implementation. The progress made and the obstacles encountered will shape not only China's future but also the global trajectory towards a sustainable low-carbon future. Further research and analysis of China's emissions reduction efforts, including its renewable energy investments and its carbon pricing schemes, are crucial to inform effective climate policy both domestically and internationally. Let's stay informed about China's emissions reduction efforts and their profound implications for the future of our planet.

Featured Posts
-
 The Importance Of Support Linda Evangelistas Journey After Mastectomy
Apr 25, 2025
The Importance Of Support Linda Evangelistas Journey After Mastectomy
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Melissa Mortons Garden Design At The Harrogate Spring Flower Show
Apr 25, 2025
Melissa Mortons Garden Design At The Harrogate Spring Flower Show
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Oklahoma City Road Conditions Watch For Ice And Accidents
Apr 25, 2025
Oklahoma City Road Conditions Watch For Ice And Accidents
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Pope Francis Impact A Refugee Familys Journey To A New Life
Apr 25, 2025
Pope Francis Impact A Refugee Familys Journey To A New Life
Apr 25, 2025 -
 St Pauli Vs Bayern Munich Sane Shines In High Scoring Victory
Apr 25, 2025
St Pauli Vs Bayern Munich Sane Shines In High Scoring Victory
Apr 25, 2025
